1. Introduction
Afghanistan is a landlocked country of great historical significance situated at the intersection of Central, South, and Western Asia. This nation, which combines nomadic customs with urban vitality, is well-known for its untamed mountains, historic Silk Road legacy, and cultural tenacity. Afghanistan’s rich tapestry of ethnicity, art, and natural beauty is equally compelling and merits a closer examination, despite frequently making headlines for geopolitical reasons.
2. Historical Overview
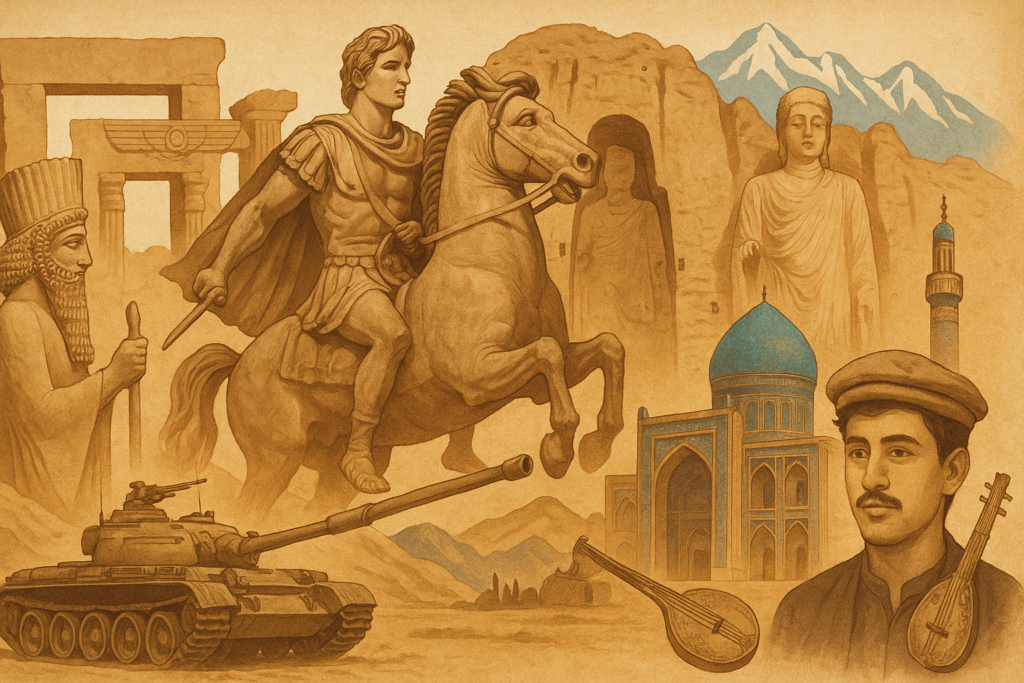

Empires and conquerors such as the Achaemenid Persians (6th century BCE) have called Afghanistan home.
- In the fourth century BCE, Alexander the Great
- Islamic, Sassanian, Kushan, and Mauryan Caliphates
- The Ghaznavids, Timurids, and Mughals also rose to prominence at this nexus of civilisations. Its modern history was shaped by Russian and British influences in the 19th and 20th centuries. Afghanistan became a kingdom after gaining independence from Britain in 1919, followed by a republic and a communist state. It then went through civil war, Soviet occupation (1979–1989), Taliban rule, a U.S.-led invasion (2001), and a Taliban comeback (2021).
Timeline Highlights
- Alexander the Great conquered it around 330 BCE.
- Ahmad Shah Durrani founded the modern Afghan state in 1747.
- Independence from British influence in 1919
- Soviet occupation from 1979 to 1989
- The first Taliban government, 1996–2001
- U.S. and NATO presence from 2001 to 2021
- 2021: Taliban rule returns
3. Geography & Climate
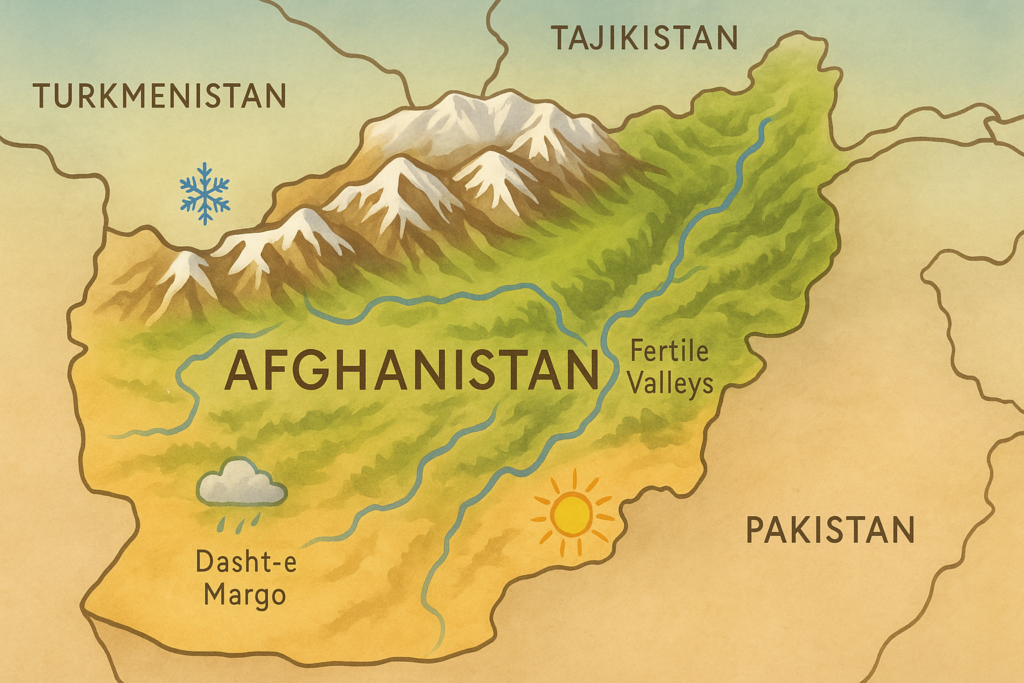
Location & Borders
- Continent: Asia (Central & South Asia)
- Neighboring countries:
- North: Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan
- East: China (Panjshir Corridor)
- South & Southeast: Pakistan
- West: Iran
- North: Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan
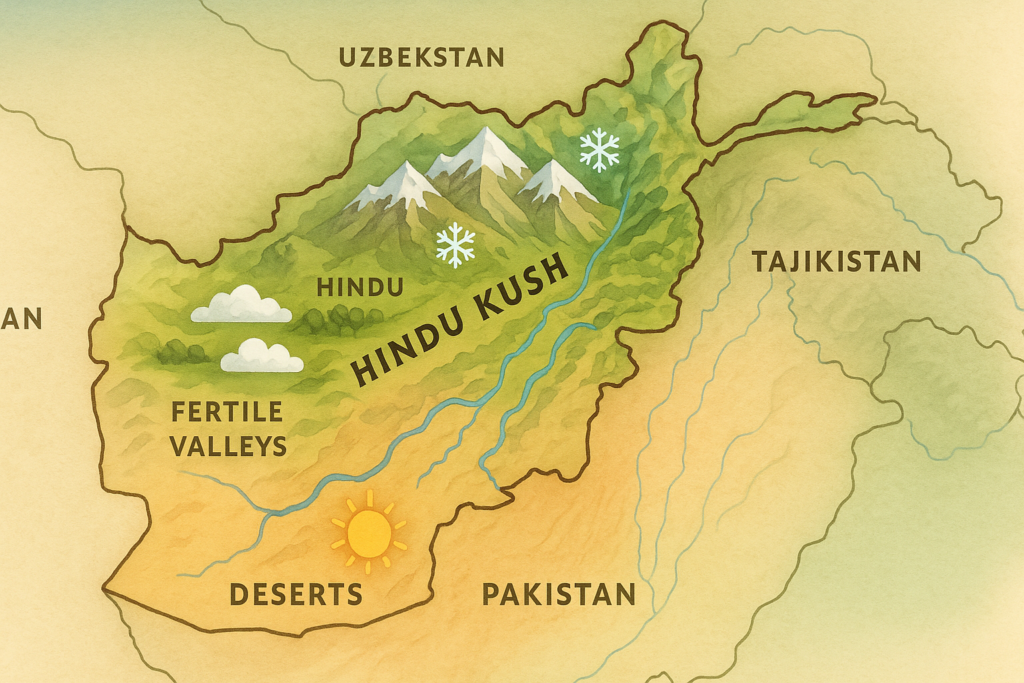
Topography
- Mount Noshaq, which reaches a peak of about 7,492 meters, is dominated by the Hindu Kush range.
- The Helmand, Herat, and Kabul Basin valleys are examples of plains.
- The climate is arid to semi-arid, with hot summers in the lowlands and cold highlands.
Climate Zones
| Region | Climate Type | Notes |
| Highlands | Continental, cold winters | Snow-covered peaks |
| Lowland Plains | Arid to semi-arid | Hot summers, low annual rainfall |
| Southern Desert | Hot desert | Temperatures > 40 °C in summer |
4. Political Structure & UN Membership
- System: Taliban-run de facto theocratic emirate
- Capital claimed: Kabul
- Leadership: Habibullah Akhundzada, the Supreme Leader
- Although its representation and recognition have changed under successive governments, Afghanistan is still a member of the UN, having joined on November 19, 1946.
- affiliated with SAARC and ECO, but currently has limited participation; not a member of major economic unions.
*Note: The international status remains complex post-2021 regime change.
5. Demographics & Language
- Population: ~40 million (2025 estimate)
- Major Ethnic Groups:
- Pashtun (~42%)
- Tajik (~27%)
- Hazara (~9%)
- Uzbek & others (~22%)
- Pashtun (~42%)
- Languages:
- Official: Pashto, Dari (Persian dialect)
- Widely Spoken: Uzbeki, Turkmen, Balochi, Pashayi
- Official: Pashto, Dari (Persian dialect)
6. Culture & Traditions
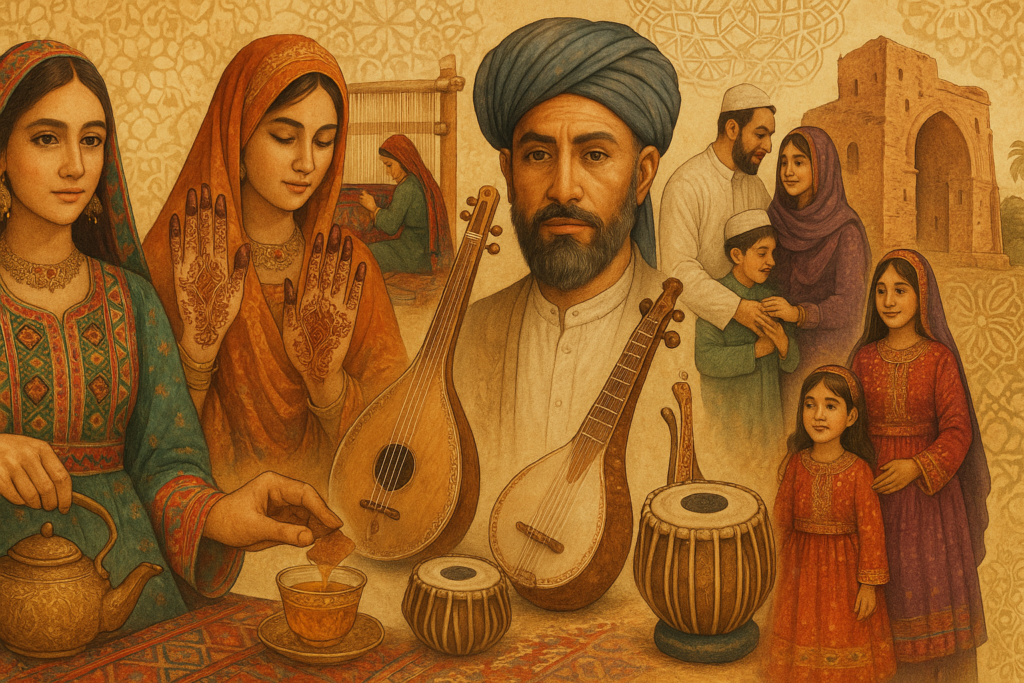

Religion & Festivals
- Main religion: Islam (Sunni ~85%, Shia ~15%)
- Major Holidays:
- Eid al-Fitr – Celebrated at Ramadan’s end
- Eid al-Adha – Commemorating Ibrahim’s sacrifice
- Eid al-Fitr – Celebrated at Ramadan’s end
Art, Music & Handicrafts
- Rich customs in embroidery (such as Herat and Kandahar motifs) and rug weaving
- Madrigal/folkloric songs (rawab, dambura) and classical court music (influenced by Hafiz Shirazi) are examples of music.
- Poetry by contemporary poets, Khushal Khan Khattak, and Rumi
Cuisine
- Mainstays include naan bread, meat stews, and rice (kabuli pulao).
- Baklava and Sheer Khurma are examples of sweets.
- Drinks: Doogh (yoghurt drink) and cardamom-infused green tea
7. Economy & Industry
- GDP (nominal): ~$25 billion (2024 est.)
- Main sectors:
- Agriculture: wheat, nuts (pistachios), and fruits (grapes, pomegranates)
- Mining: coal, marble, lithium potential, copper (Mes Aynak), and
- Crafts: jewellery, carpets, and textiles
- Informal: cross-border trade, livestock
- Key Challenges:
- Unrest in politics
- After 2021, sanctions
- Absence of global banking
- High rates of unemployment and poverty
- Aid: Dependent on foreign aid
8. Major Cities
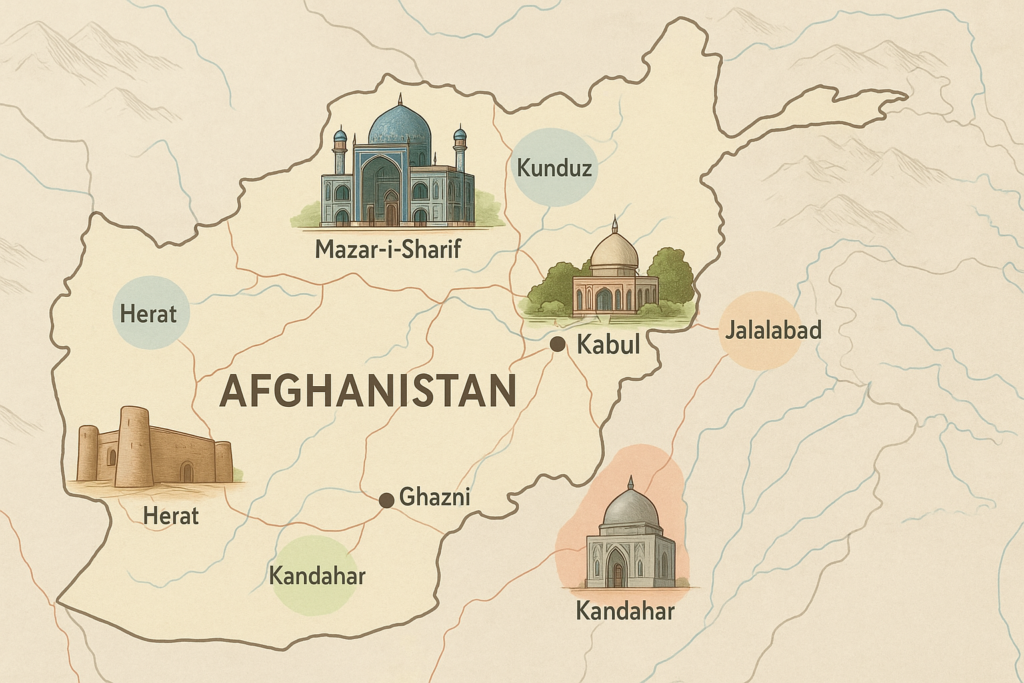
Kabul
- capital with a population of about 4 million
- Babur Gardens and the National Museum are located in this cultural and commercial centre.
Kandahar
- Pashtun culture’s stronghold in the South
- The Durrani Empire’s historical centre
Herat
- renowned for its Friday Mosque, Islamic architecture, and cultural celebrations
Mazar-i-Sharif
- renowned for the SEK international border gateway and the Blue Mosque of Hazrat Ali
Jalalabad
- Fruit orchards and a horticulture centre in the eastern city close to Khyber Pass
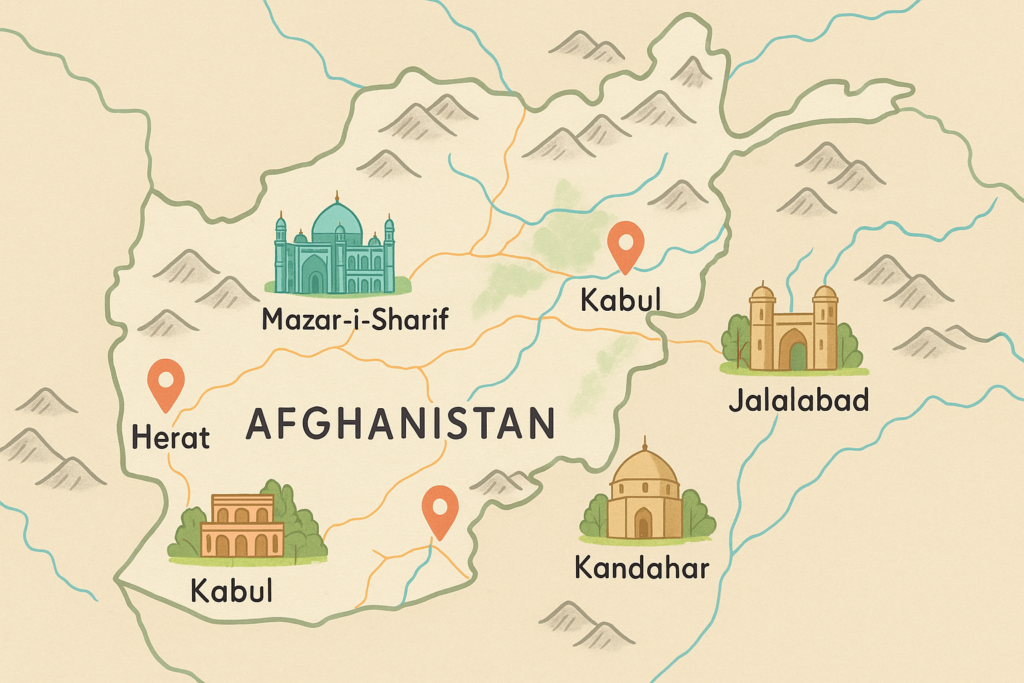
9. Tourist Attractions
- Buddhas and the Bamyan Valley: UNESCO site of carved stone statues destroyed in 2001
- The UNESCO-listed Minaret of Jam dates back to the 12th century.
- Kabul’s Babur Gardens are botanical gardens from the Mughal era.
- Friday Mosque and Herat Citadel: magnificent Timurid architecture
- Panjshir Valley is a serene, picturesque mountain valley.
- The six blue, high-altitude lakes of Band-e Amir
- Kandahar Shrine of Prophet Muhammad’s Cloak
10. Unique Facts
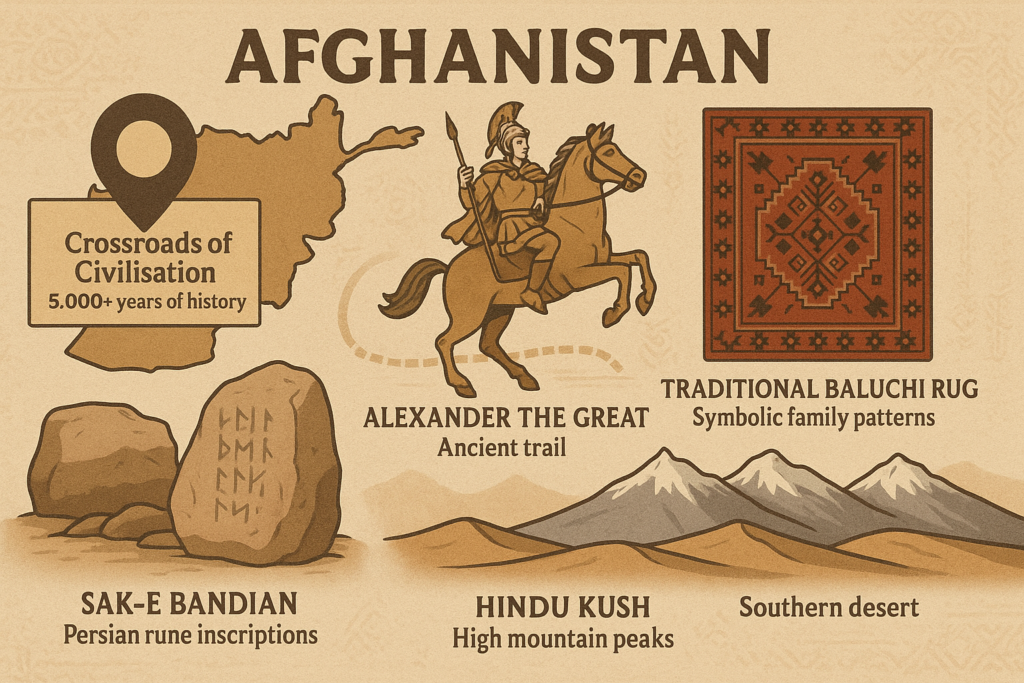
- Crossroads of Civilisation: More than 5,000 years of recorded history
- Alexander the Great travelled through its territories.
- Family heritage is passed down through rug patterns, such as Baluchi designs.
- Rune inscriptions on Sak-e Bandian rocks (pre-Islamic Persian influences)
- Extreme altitude range: mountains above 7,490 m and deserts
11. Challenges & Future Outlook
Key Issues
- Taliban rule and political unrest
- Restricted rights for women and minorities
- Loss of international access and economic stagnation
- Security issues, particularly those posed by ISIS-K
International Mission
- Demands for UN involvement and humanitarian assistance
- Afghanistan aims for stability by limiting trade and reopening banks gradually.
- Long-term objectives: reconstruction, women’s rights reforms, and resurrected mining
12. Conclusion
Afghanistan is a prime example of both persistent fortitude and difficult problems. Its magnificent scenery, ancient culture, and diverse population stand in sharp contrast to the continuous humanitarian crises and unpredictability. Afghanistan’s future depends on striking a balance between internal reform, diplomacy, and tradition as the world looks on. However, its human capital, strategic significance, and cultural contributions provide a basis for a more optimistic future.
- Neighboring Countries
- Iran
- Pakistan
- China
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
- Turkmenistan
- Iran
- Related Content:
- All 195 Countries List with Maps
- Asian Countries Overview
- UN Member States Explained
- Top Tourist Places in Asia
- All 195 Countries List with Maps
- UN Membership:
https://www.un.org/en/about-us/member-states - World Bank Country Profile:
https://data.worldbank.org/country/afghanistan - CIA World Factbook – Afghanistan:
https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/afghanistan/ - UNESCO Sites in Afghanistan:
https://whc.unesco.org/en/statesparties/af - Travel Advisory (U.S. Gov):
https://travel.state.gov
BBC Country Profile:
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-south-asia-12024253 👈




[…] 1.Afghanistan: A Deep Dive Into Its History, Culture & Landscape […]
[…] 1.Afghanistan: A Deep Dive Into Its History, Culture & Landscape […]
[…] 1.Afghanistan: A Deep Dive Into Its History, Culture & Landscape […]
[…] 1.Afghanistan: A Deep Dive Into Its History, Culture & Landscape […]
[…] 1.Afghanistan: A Deep Dive Into Its History, Culture & Landscape […]