Introduction
Angola is a fascinating nation in southern Africa that skilfully combines a rich cultural heritage, rapid economic development, and stunning natural scenery with a deeply ingrained past. Angola has something to offer every traveler, student, and business owner, from its significant status as a Lusophone African country to its vibrant cities and amazing tourist attractions. We delve deeply into Angola’s history, geography, language, culture, economy, and tourist attractions in this guide.

🗺️ Geographic Location & World Position
Continent & Coordinates
Situated on Africa’s southwest coast, Angola shares a diverse range of landscapes with the Atlantic Ocean, ranging from vast highlands and dense rainforests to coastal plains.
Neighboring Countries
- North: Republic of Congo (Congo-Brazzaville), Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC)
- East: Zambia
- South: Namibia
- West: Atlantic Ocean
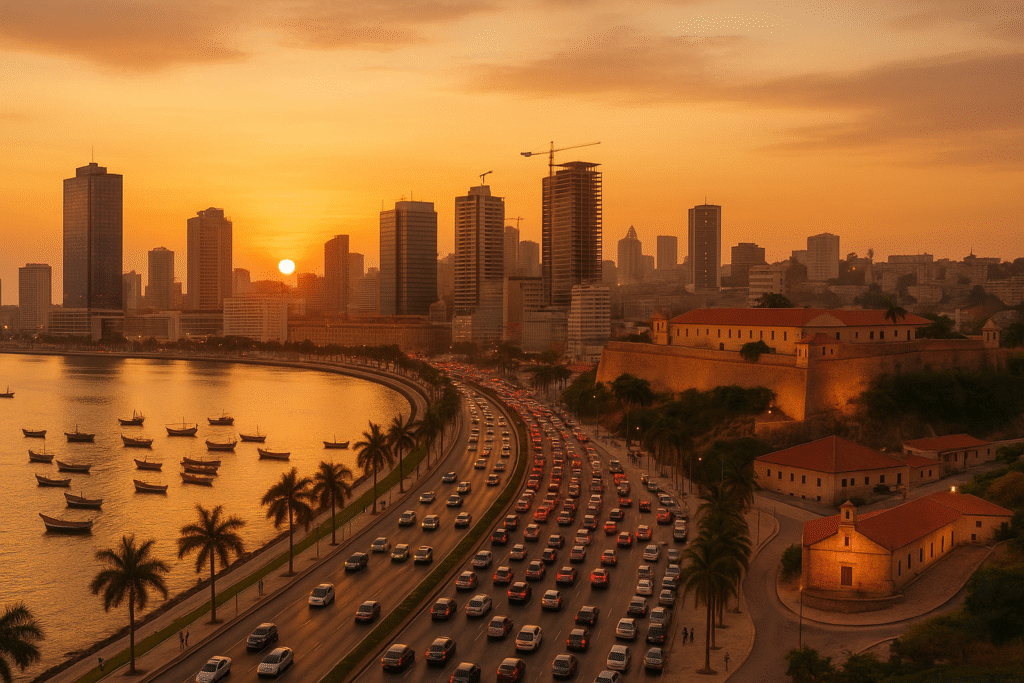
The nation’s link to international trade routes and maritime heritage is anchored by Luanda, its coastal capital.

🇺🇳 United Nations Membership
Shortly after separating from Portugal, on December 1, 1975, Angola became a member of the United Nations. Additionally, it belongs to the Southern African Development Community (SADC), the Community of Portuguese Language Countries (CPLP), and the African Union.
📜 Historical Overview
Pre-Colonial & Kingdom Era
- Bantu-speaking peoples lived in the area and founded kingdoms like Kongo, Ndongo, and Matamba.
- These kingdoms interacted politically and economically early on and had sophisticated systems of government.
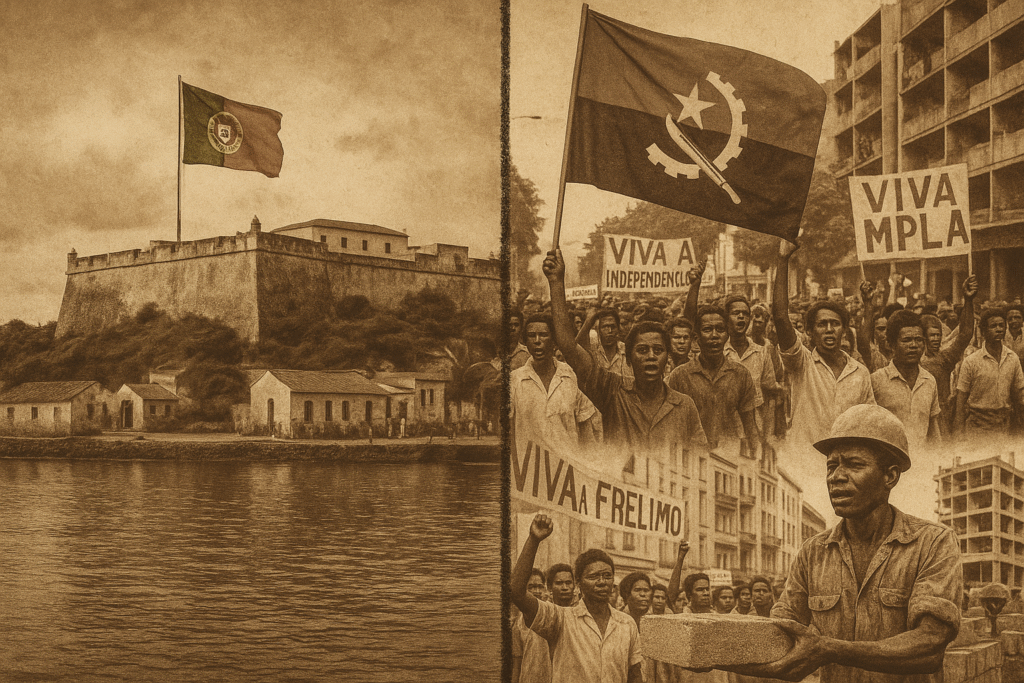
Portuguese Colonization (1575–1975)
- Luanda was founded in 1575, marking the start of centuries of Portuguese domination.
- A key player in the Atlantic slave trade was Angola.
- Oil, coffee, and rubber also became important exports during the colonial era.
Independence & Civil War
- On November 11, 1975, Angola proclaimed its independence.
- The FNLA, UNITA, and the ruling MPLA were involved in the nearly three decades of civil war that followed.
- With the formal end of the war in 2002, a phase of development and reconstruction began.
Post-War Era
- Angola concentrated on diversifying its economy and repairing its infrastructure.
- Since then, it has experienced major economic reforms and urban development, increasing its prominence on the African continent.
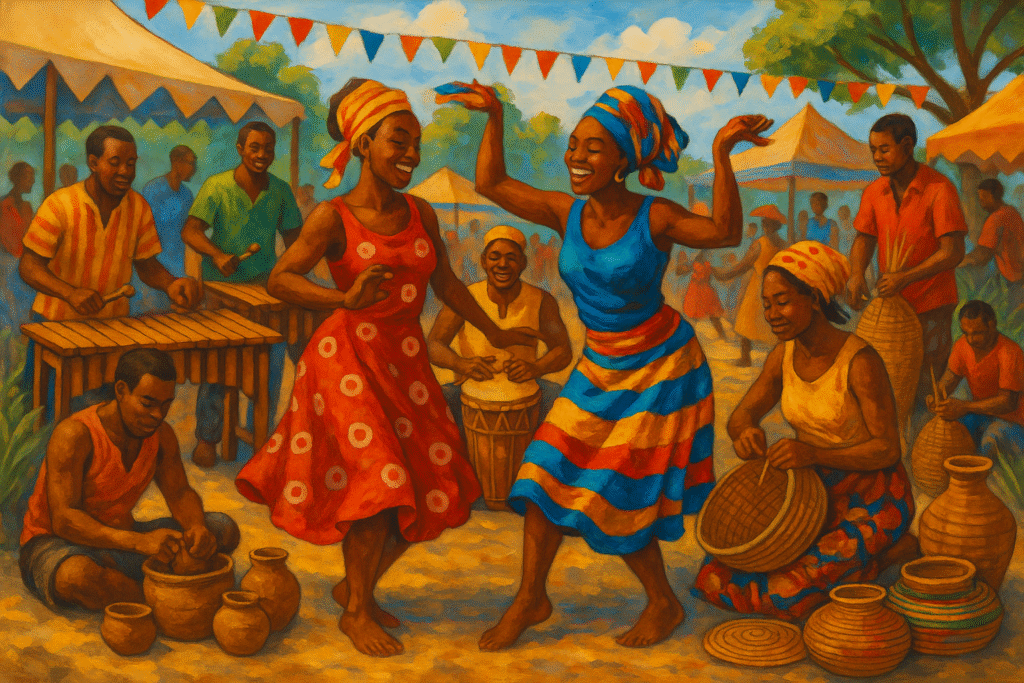
🌍 Major Cities & Regions
- Luanda – The largest and capital city; the centre of the economy and culture.
- Huambo – agricultural centre in the central highlands.
- Benguela & Lobito – important seaside cities with important ports.
- Lubango – a cultural hub and picturesque highlands.
- Malanje – entrance to the Bolongongo Plateau and Kissama foothills.
🎭 Culture & Society

Ethnolinguistic Diversity
There are more than 100 ethnic groups in Angola. Bakongo, Chokwe, Mbundu, and Ovimbundu are important ones.
Language
- Portuguese is the official language.
- Umbundu, Kimbundu, Kikongo, Chokwe, and other regional and national languages.
- Portuguese coexists with regional dialects, enhancing cultural expression.
Religious Beliefs
- Christianity (Catholicism and Protestantism) is practiced by about 95% of people.
- In local customs, Christianity and indigenous beliefs frequently coexist.
Arts & Music
- rich customs in the visual arts, dance, and music.
- The genres of Kuduro, Semba, and Kizomba are well-known throughout the world.
- Regional diversity is reflected in batik textiles, pottery, wood carvings, and handcrafted weavings.
Traditions & Festivals
- National Heroes’ Day (September 17) and Independence Day (November 11) are examples of national holidays.
- Local celebrations, like Luanda’s “Semba Festival,” honour customs, music, and the harvest.

💰 Economy & Resources
Key Economic Sectors
- Oil & Gas: central to Angola’s economy, accounting for almost half of government income and more than 90% of exports.
- Diamonds: among the leading producers in the world.
- Agriculture: Coffee, bananas, maize, cassava, and palm oil are examples of staple crops.
- Mining: Phosphate, copper, gold, iron ore, and more.
Infrastructure & Development
- significant expenditures on refinery projects, ports of Lobito and Luanda, railroads, and roads.
- Foreign investors are drawn to a number of tax breaks and Economic Free Zones.
Economic Challenges
- Because of its heavy reliance on oil, the economy is susceptible to changes in its price globally.
- Access to healthcare, youth unemployment, and social inequality all need to be improved.
- The goal of ongoing economic reforms is to encourage growth in the private sector and diversify..
✈️ Tourist Attractions
Luanda & Surroundings
- The 16th-century monument known as the Fortress of São Miguel offers expansive views.
- The eccentric cast-iron palace known as the Palácio de Ferro is credited to Eiffel.
- The vibrant culture of Luanda is reflected in the Crystal Palace and the Marginal Promenade.
Central Highlands & Lobito
- Lubango is well-known for its breathtaking mountain views and the Cristo Rei monument.
- An iconic scenic overlook is Tundavala Gap.
- Between Lobito and Huambo, the Benguela Railway offers breathtaking views.
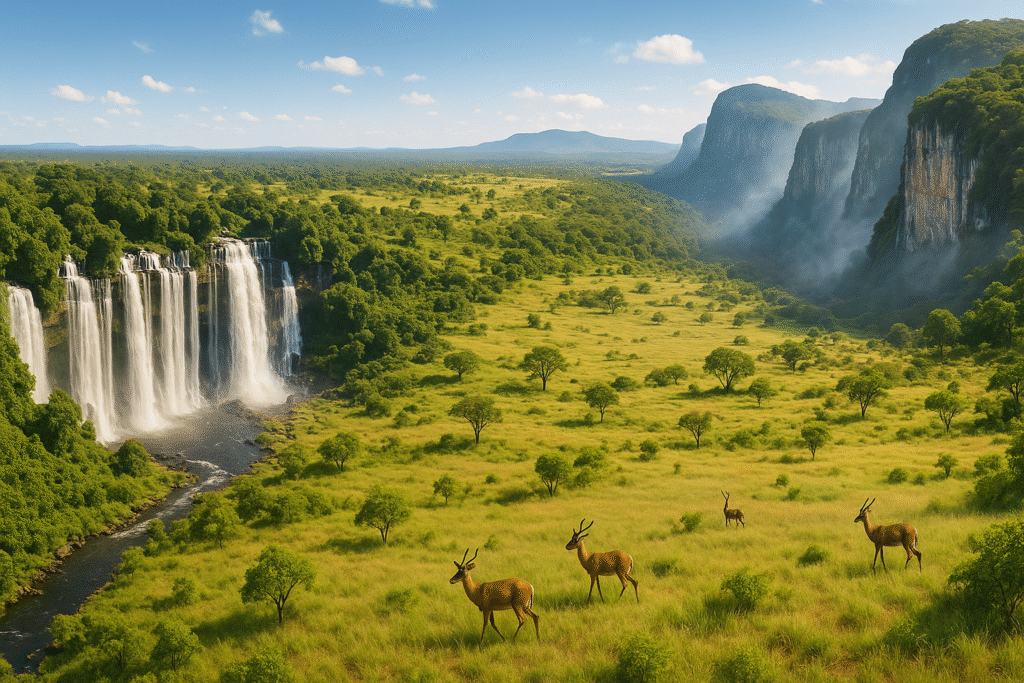
Inland Treasures
- One of the biggest waterfalls in Africa is Kalandula Falls.
- Birdwatching and biodiverse wetlands can be found at Miranda Eco Reserve.
- Experience a safari with antelope, lions, and elephants in Kissama National Park.
Northern Angola
- UNESCO-designated sites include the Mbanza Kongo Ruins and the Congo River source.
- There are wood-carving villages and traditional marketplaces all over.

🗣️ Language & Communication
- Portuguese is widely used in government, the media, and schools.
- regional languages that are spoken in everyday life and in schools.
- Tourists benefit from multilingual signage.
📌 Unique & Interesting Facts
- Lusophone Influence: After Brazil, Angola is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking nation.
- Rapid Urbanization: Because of its oil wealth and the demand from expatriates, Luanda is among the most expensive cities in the world.
- Kizomba’s Origins: The popular dance/music style has its origins in Angola.
- Resilient Wildlife: Wildlife in national parks is still recovering from the war.
- Pataca Currency: Prior to gaining independence, Angola used Portuguese colonial money.
- New Borders: The ongoing conflict with the DRC over the island of Ingua is amicable.

📌 Angola’s Role in Global Affairs
- voting member of OPEC, the CPLP, the African Union, and the UN.
- supporter of African Union development initiatives and UN peacekeeping missions.
✅ Conclusion
The tale of Angola is one of triumphing over hardship to restore identity and spur development. It is positioned as a major player in Africa’s future due to its strategic coastal assets, resource-driven economy, and rich cultural legacy. Angola promises a journey of discovery, resiliency, and vibrancy, whether you’re exploring the urban bustle of Luanda, taking in the views of Kalandula Falls, or dancing to the rhythms of Kizomba.
🔗 Final Thoughts
A nation that has been healed from widespread conflict and is ready to embrace modernity while respecting its heritage, Angola is a mosaic of languages, landscapes, and lifeways. Angola is just waiting to be discovered, whether it is through its history, culture, economy, or natural beauty.

- Official Government Portal of Angola
http://www.governo.gov.ao
(News, policies, national initiatives – Portuguese) - CIA World Factbook – Angola
https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/angola/
(Up-to-date geopolitical, economic, and demographic data) - UNESCO Angola Profile
https://whc.unesco.org/en/statesparties/ao
(UNESCO sites and cultural heritage) - Angola Tourism Official Site (if available)
https://www.visitangola.net (unofficial, but informative)
(Travel tips, destinations, and experiences) - World Bank – Angola Overview
https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/angola
(Economic outlook, development projects, and statistics)
BBC Country Profile – Angola
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-13036732
(Political, cultural, and historical background)




